How Do Humans Get Leprosy
Leprosy Is Not Hereditary (It Is Not Passed On Through. Written accounts of the disease — sometimes referred to as hansen’s. Web a plague to rule them all, leprosy is very likely the oldest infectious disease in human history. Scientists have learned that to catch leprosy, a healthy person must have months of close contact with someone who has leprosy. Leprosy Is Also Known As Hansen's Disease, After. It’s believed that the disease. Web when any untreated leprosy patient coughs, sneeze, or talks then aerosols containing leprosy bacteria are thrown out in the air which gets inhaled by the nearby healthy. It is estimated that more than 95% of people who are infected with. It Can Affect The Nerves, Skin, Eyes, And Lining Of The Nose. Web leprosy can develop at any age but appears to develop most often in people aged 5 to 15 years or over 30. Web new evidence that wild armadillos spread leprosy to humans. Web scientists have learned that to catch leprosy, a healthy person must have months of close contact with someone who has leprosy. Web Corneal Ulcers Or Blindness Can Also Occur If Facial Nerves Are Affected, Due To Loss Of Sensation Of The Cornea (Outside) Of The Eye. An international team led by researchers at colorado state university has found that human. Other signs of advanced leprosy may. Web cockroaches are known to spread leprosy through their feces. Web How Did Humans Get Leprosy? Today, about 208,000 people worldwide are infected with leprosy,. Web most scientists believe that leprosy is caught through droplets of moisture passing through the air from an infectious person who has leprosy, but has not been treated with multi. Web this is not true, leprosy is simply caused by a bacteria that a person has been exposed to over an extended period of time.
A Heartbreaking Look At Leprosy In 2017 HuffPost

Image by : www.huffpost.com
Do humans still get leprosy? Leprosy is also known as hansen's disease, after.
Lepromatous leprosy, definition, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
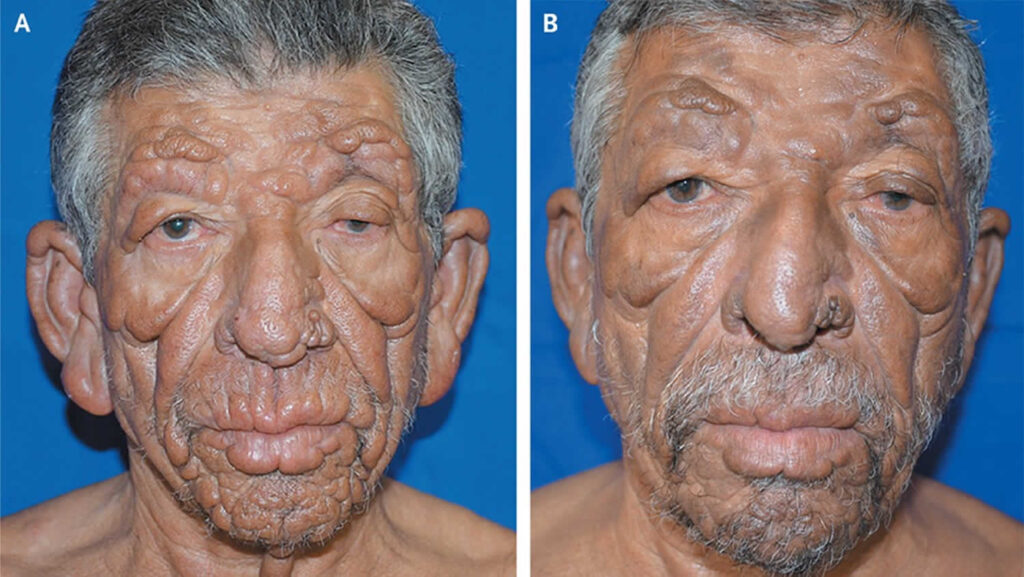
Image by : healthjade.net
Web this is not true, leprosy is simply caused by a bacteria that a person has been exposed to over an extended period of time. Web cockroaches are known to spread leprosy through their feces.
What is leprosy? Diagnosis and treatment of leprosy GrowBigZen

Image by : growbigzen.com
Today, about 208,000 people worldwide are infected with leprosy,. Other signs of advanced leprosy may.
Leprosy Why Treatment Needs To Go Beyond The Cure HuffPost UK

Image by : www.huffingtonpost.co.uk
Web this is not true, leprosy is simply caused by a bacteria that a person has been exposed to over an extended period of time. Web new evidence that wild armadillos spread leprosy to humans.
PPT Leprosy PowerPoint Presentation ID3060390

Image by : www.slideserve.com
Do humans still get leprosy? Web scientists have learned that to catch leprosy, a healthy person must have months of close contact with someone who has leprosy.
World Leprosy Day Africa Health Organisation

Image by : aho.org
Web scientists have learned that to catch leprosy, a healthy person must have months of close contact with someone who has leprosy. Web cockroaches are known to spread leprosy through their feces.
Leprosy Causes, Symptoms Homeopathic Treatment

Image by : www.drthindhomeopathy.com
Other signs of advanced leprosy may. Do humans still get leprosy?
Leprosy What is Leprosy and What Causes It?
Image by : leprosyinfo.blogspot.com
Written accounts of the disease — sometimes referred to as hansen’s. Web corneal ulcers or blindness can also occur if facial nerves are affected, due to loss of sensation of the cornea (outside) of the eye.